Summary by James R. Martin, Ph.D., CMA
Professor Emeritus, University of South Florida
Fascism Main Page |
Political Issues Main Page
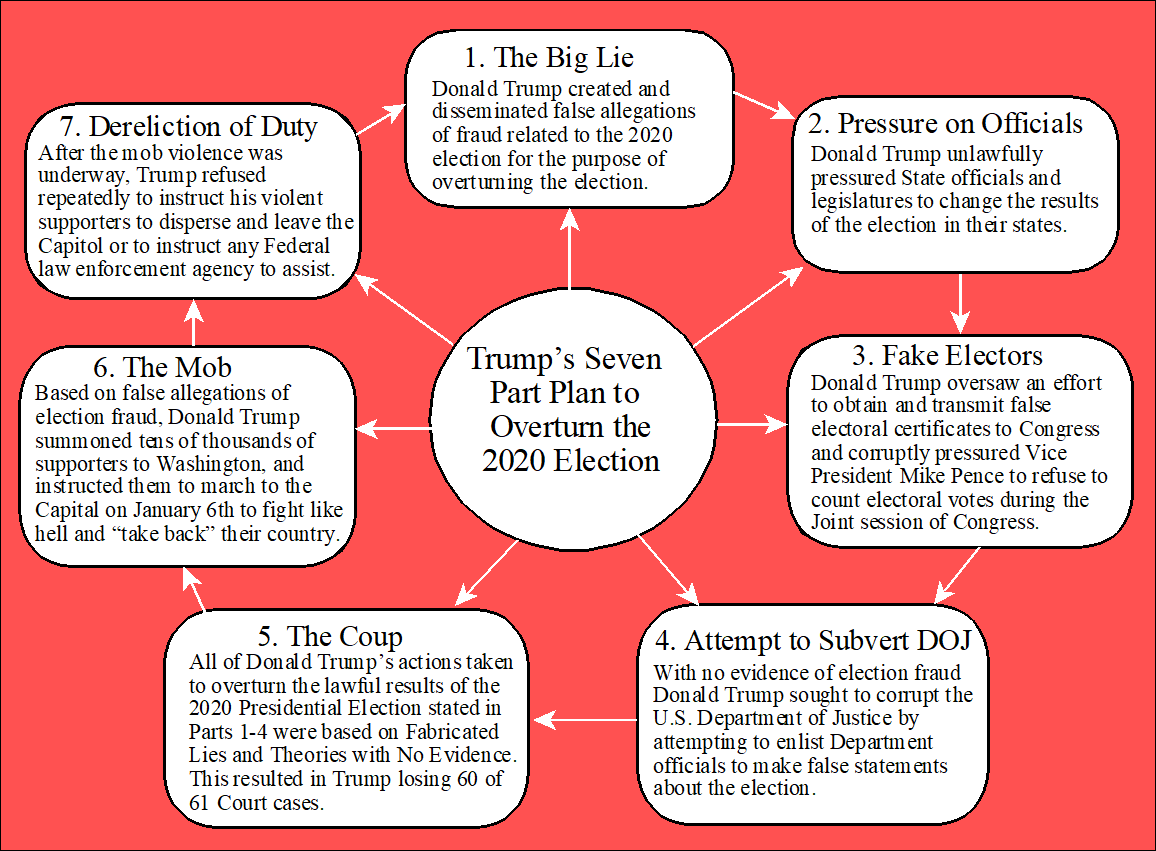
The Seven Part Plan to Overturn the 2020 U.S. Presidential Election
1. Trump's Big Lie - Donald Trump created and disseminated false allegations of fraud related to the 2020 election for the purpose of overturning the election, and to solicit contributions from those who would believe his lies. He refused to accept the lawful result of the 2020 election even though his senior advisors refuted his election fraud claims. Instead Trump plotted to overturn the election outcome. He planned to use the “red mirage” that normally occurs in elections as a reason to claim an early victory. Republicans tend to vote in person on election day and those votes are counted first. Democrats tend to vote early and use mail-in voting. Those votes are counted last, so it appears that the Republican candidate is leading early in the race, i.e., the “red mirage.” Trump continued with a blizzard of lies and statements delegitimizing mail-in voting. Trump has continued with the lies and conspiracy theories (e.g., that voting machines were flipping votes) for over three years even though his campaign team told him that he lost the election and that there was no significant fraud. Trump lost 61 of 62 court cases in nine states, and the Supreme Court rejected his fraud claims.
2. Trump's Pressure to Find votes - Donald Trump unlawfully pressured State officials and legislatures to change the results of the election in their states. Undeterred by the facts, Trump pressured Georgia Secretary of State Brad Raffensperger to overturn the Georgia results telling Raffensperger that not reporting the fraud was illegal, and that he should find enough votes (11,780) to declare Trump the winner of an election that he lost. Raffensperger saw this as a threat. Trump made similar calls to state officials in several other states. For example, Trump also called the Governor of Arizona (Doug Ducey) and urged him to overturn the state’s election results.
3. Trump's Fake Electors - Donald Trump oversaw an effort to obtain and transmit false electoral certificates to Congress and the National Archives. Knowing that it would be illegal, Trump corruptly pressured Vice President Mike Pence to refuse to count electoral votes during the Joint session of Congress. Trump also pressured Members of Congress to object to valid slates of electors from several states, and he purposely verified false information filed in Federal court. The Vice President and members of the Congress do not have the authority to overturn the results of an election. The 12th Amendment states that the President of the Senate opens the ballots in the joint session and the votes are then counted. According to the Constitution, the roles of the VP and Congress are purely ministerial.
4. Trump's Attempt to Subvert the DOJ - With no evidence of election fraud Donald Trump sought to corrupt the U.S. Department of Justice by attempting to enlist Department officials to make false statements about the election. Trump told Jeffrey Rosen (Acting Attorney General after William Barr resigned) and Richard Donoghue (Acting U.S. Deputy Attorney General) to “just say the election was corrupt and leave the rest to me and the Republican Congressmen.” Trump offered the position of Acting Attorney General to Jeff Clark (a lower level employee in the DOJ) who intended to disseminate false information aimed at overturning the election.
5. Trump's Coup with Fabricated Theories and No Evidence - All of Donald Trump’s actions stated above were taken in support of a multi-part conspiracy to overturn the lawful results of the 2020 Presidential Election. The various theories of how the election was stolen (votes switched by voting machines, dead voters, more votes than registered voters, etc.,) were ruled on in 61 court cases. Donald Trump lost 60 of those cases and the case that he won revealed nothing that would have changed the results of the election. Many of the judges in these cases explicitly indicated in their decisions that the evidence presented by the plaintiffs was wholly insufficient on the merits. Rusty Bowers (Speaker of the Arizona State House of Representatives) testified that Rudy Giuliani eventually admitted that “We’ve got lots of theories, we just don’t have the evidence.”
6. Trump's Mob - Based on false allegations of election fraud, Donald Trump summoned tens of thousands of supporters to Washington (including The Proud Boys, The Oath Keepers, White Nationalists, Three Percenters, and QAnon), and instructed them to march to the Capital on January 6th to fight like hell and “take back” their country. During the attack on the Capital Donald Trump sent a social media message publicly condemning Vice President Pence. Trump said Pence didn't have the courage to do what should have been done to protect the country. Shortly after Trump's tweet the mob began chanting "Hang Mike Pence!" and broke into the Capital. Donald Trump knew that the Vice President had no legal authority to prevent certification of the election, but he continued to act with a corrupt purpose.
7. Trump’s Dereliction of Duty - After the mob violence was underway, Trump refused repeatedly to instruct his violent supporters to disperse and leave the Capitol. Instead he watched the attack on television. His dereliction of duty to ensure that laws are faithfully executed perpetuated the violence at the Capital and obstructed Congress’s proceedings to count the electoral votes. Trump had the authority and responsibility to direct deployment of the National Guard in the District of Columbia, but he did not give the order. In addition Trump did not instruct any Federal law enforcement agency to assist, not at the Pentagon, not at the Department of Homeland Security, the Department of Justice, the F.B.I, the Capital Police Department, or the D.C. Mayor's office. In addition, he did not order any of his staff to facilitate a law enforcement response.

_____________________________
* Thompson, B. G., L. Cheney, Z. Lofgren, A. B. Schiff, P. Aguilar, S. N. Murphy, J. Raskin, E. G. Luria and A. Kinzinger. 2022. Final Report of the Select Committee to Investigate the January 6th Attack on the United States Capital. U. S. House of Representatives. U.S. Government Publishing Office, Washington DC. (GPO-J6-Report.pdf). Some of this summary is based on additional information in Liz Cheney's 2023 book. Her Chapter 43 is titled Seven-Part Plan. See Cheney, L. 2023. Oath and Honor: A Memoir and a Warning. Little Brown and Company.
Related summaries:
A Post About Trump and Various Issues That Are Non-Debatable
Anonymous. 2019. A Warning: A Senior Trump Administration Official. Twelve: Hachette Book Group. (Summary).
Crossan, M., W. Furlong and R. D. Austin. 2022. Make leader character your competitive edge. MIT Sloan Management Review (Fall): 1-12. This article includes a leader character framework. (Summary).
Martin, J. R. Not dated. Policies of a Second Trump Presidency.
Martin, J. R. Not dated. Shepard Fairey Political Posters.
Martin, J. R. Not dated. Summary of what Trump is and what he is not.
Martin, J. R. Not dated. Why I vote for Democrats.
Rosenfeld, G. D. (Editor) and J. Ward (Editor). 2023. Fascism in America: Past and Present. Cambridge University Press. (Summary).
Stanley, J. 2018. How Fascism Works: The Politics of Us and Them. Random House. (Summary).